Health Equity

What is Health Equity?
Health equity means achieving the highest level of health for all people and shall entail focused efforts to address avoidable inequalities by equalizing conditions of health for those who have experienced injustices, socioeconomic disadvantages, and systemic disadvantages. Health equity is about addressing the needs experienced by individuals and communities.
What are Health Disparities?
There are many definitions of health disparities.
Health disparities means measurable differences in health status, access to care, and quality of care as determined by race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, gender identity, a preferred language other than English, gender expression, disability status, aging population, immigration status, and socioeconomic status.
Healthy People 2020, which is a set of objectives to improve the health of all Americans established every decade, defined a health disparity as: "a particular type of health difference that is closely linked with social, economic, and/or environmental disadvantage. Health disparities adversely affect groups of people who have systematically experienced greater obstacles to health based on their racial or ethnic group; religion; socioeconomic status; gender; age; mental health; cognitive, sensory, or physical disability; sexual orientation or gender identity; geographic location; or other characteristics historically linked to discrimination or exclusion." (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services)
Another definition of health disparities comes from the National Institutes of Health. Health disparities are differences in the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and burden of diseases and other adverse health conditions that exist among specific population groups in the United States.
Health disparities can result from multiple social determinants of health. Read more Frequently Asked Questions.
What are Social Determinants of Health?
Social determinants of health means life-enhancing resources, such as availability of healthful foods, quality housing, economic opportunity, social relationships, transportation, education, and health care, whose distribution across populations effectively determines the length and quality of life.
The social determinants of health are the circumstances in which people are born, grow up, live, work, and age, as well as the systems put in place to deal with illness (World Health Organization, 2012). Social determinants of health include: poverty; environmental threats; inadequate access to health care; individual and behavioral factors; and educational inequalities. Social determinants of health are influenced by a wider set of forces including economics, social policies, and politics. Read more Frequently Asked Questions..
Click so see a text version of the image above
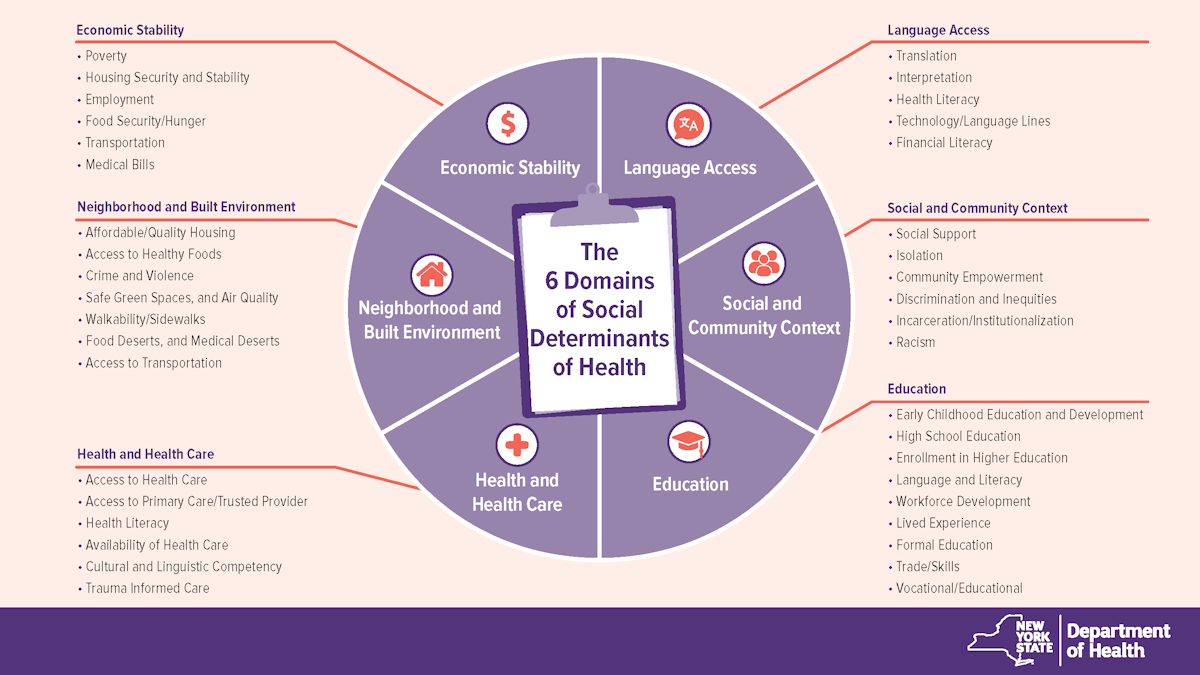
The 6 Domains of Social Determinants of Health
Economic Stability
- Poverty
- Housing Security and Stability
- Employment
- Food Security/Hunger
- Transportation
- Medical Bills
Neighborhood and Built Environment
- Affordable/Quality Housing
- Access to Healthy Foods
- Crime and Violence
- Safe Green Spaces, and Air Quality
- Walkability/Sidewalks
- Food Deserts, and Medical Deserts
- Access to Transportation
Health and Health Care
- Access to Health Care
- Access to Primary Care/Trusted Provider
- Health Literacy
- Availability of Health Care
- Cultural and Linguistic Competency
- Trauma Informed Care
Language Access
- Translation
- Interpretation
- Health Literacy
- Technology/Language Lines
- Financial Literacy
Social and Community Context
- Social Support
- Isolation
- Community Empowerment
- Discrimination and Inequities
- Incarceration/Institutionalization
- Racism
Education
- Early Childhood Education and Development
- High School Education
- Enrollment in Higher Education
- Language and Literacy
- Workforce Development
- Lived Experience
- Formal Education
- Trade/Skills
- Vocational/Educational
Prevention Agenda
The Department is working on the next iteration of the Prevention Agenda. Learn more about the State's 2019-2024 Prevention Agenda.
New York State Health Equity Reports
Health outcomes can differ among groups of people. Some groups are more negatively affected than others because of social, economic, or environmental disadvantage related to life circumstances, discrimination, or exclusion. Often times, these experiences are associated with race and/or ethnicity. The difference in health outcomes among groups is referred to as health disparity.
To address health disparities, we must first be able to identify and measure them. Having good data is critical to these efforts. The Department has been providing state and county level data on health disparities since 2007. The Health Equity Reports are a part of the Office of Minority Health and Health Disparities Prevention’s legislative charge as per Public Health Law § 242.